Arbuscular Mycorrhizal (Glomus Fasciculatum) Fungi as a Plant Immunity Booster against Fungal Pathogen
Siddharam Math1 , Sagar Arya2,3, Hiralal Sonawane1*
, Sagar Arya2,3, Hiralal Sonawane1* , Vilas Patil4, Manohar Chaskar1
, Vilas Patil4, Manohar Chaskar1
1Prof. Ramkrishna More College of Arts, Commerce and Science, Akurdi, Pune, India.
2Center for Innovation Research and Consultancy, Pune, India.
3TERI-Deakin Nano Biotechnology Centre, Gurgaon, Haryana, India.
4Dr. B.N. Purandare Arts and Smt. S.G. Gupta Commerce and Science College, Lonavala, Pune, India.
Corresponding Author Email: amolsbr@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CARJ.7.1.12
Article Publishing History
Received: 24/03/2019
Accepted: 29/04/2019
Published Online: 01/05/2019
Review Details
Reviewed by: Dr. Isna Rasdianah
Second Review by: Dr. Vikas Sharma
Final Approval by: Dr. Avtar Singh Bimbraw
Abstract:
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) mediated immune response in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) Glomus fasciculatum (GF) was studied in the presence of plant pathogenic fungi Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici (FOL). Our aim was to assess how symbiosis of AMF potentiates ROS immune response system to deal pathogen mediated biotic stress. Tomato plant was inoculated with GF, FOL and GF + FOL in separate experimental sets to examine its effect on plants ROS machinery and the time taken to alleviate biotic stress. The antioxidant response was evaluated and correlated with the time provided by GF treated plants against FOL to initiate their second line of defenses as compared to only FOL treated ones. The establishment of symbiosis and development showed a positive effect on plant ROS response system and subsequently its growth. No significant difference was seen in the root mass of only GF, FOL and GF + FOL. The increase in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase was similar in all the control and treated plants however; reduction in activities of these ROS scavengers was much faster in GF supplemented plants. Similar trend was also observed for ROS radicals possibly due to the involvement of antioxidant enzymes. LC-MS analysis of FOL was performed to co-relate the effect of some dominant compounds with its pathogenicity. Therefore, our results showcase AMF-GF’s ability to alleviate the oxidative damage generated by biotic stress and highlights on the buffer time taken by plants defense machinery to immunize itself at various levels.
Abbreviations: Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), Glomus fasciculatum (GF), Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici (FOL)
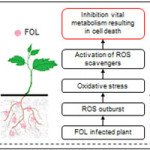 |
Graphical Abstract Click here to View Abstract |
Keywords:
Antioxidant Enzymes; Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi; Fusarium Oxysporum. Glomus Fasciculatum; Reactive Oxygen Species; Tomato Plant
| Copy the following to cite this article: Math S, Arya S, Sonawane H, Patil V, Chaskar M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (Glomus fasciculatum) fungi as a plant immunity booster against fungal pathogen. Curr Agri Res 2019;7(1). doi : http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CARJ.7.1.12 |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Math S, Arya S, Sonawane H, Patil V, Chaskar M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (Glomus fasciculatum) fungi as a plant immunity booster against fungal pathogen. Curr Agri Res 2019;7(1). Available from: https://bit.ly/2VH4Uqo |
Back to TOC
